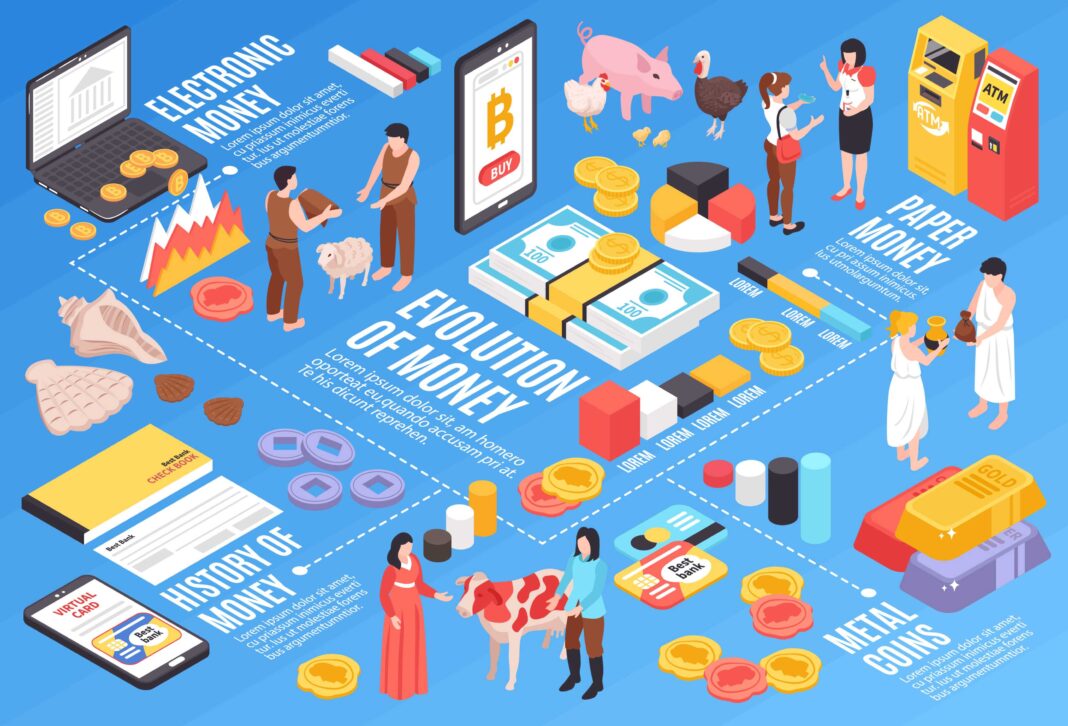
Money, as we know it today, is the result of thousands of years of innovation, trust, and adaptation. It hasn’t always been paper notes and plastic cards. In fact, the development of money has gone through several distinct stages, each shaping the way humans exchange goods and services.
Let’s take a detailed look into the main stages of Evolution of money, with real-world examples and practical insights that explain how we moved from bartering goods to digital payments in seconds.
🛒 1. Barter System: Trading Without Money
Before the invention of money, people relied on barter trade—a simple system where goods and services were exchanged directly without any medium.
🔄 How It Worked
If you had wheat and needed shoes, you had to find a shoemaker who needed wheat. This made trade time-consuming and inefficient. It worked for small communities, but as societies grew, barter became too limited.
⚠️ Challenges
- Double coincidence of wants: both parties had to need what the other offered.
- No common measure of value.
- Difficult to store wealth.
🪙 2. Commodity Money: Using Objects with Value
As barter lost efficiency, societies began using items that had intrinsic value as money. This stage introduced commodity money—objects used for trade that also had value in themselves.
🐚 Examples of Commodity Money
- Cowry shells in Africa and Asia
- Salt in ancient Rome (even the word salary comes from “sal”—Latin for salt)
- Metal tools, cattle, and even rice
✅ Benefits
- More widely accepted than barter
- Portable and had recognized value
Yet, commodities still had limitations—they could spoil (like food), or were difficult to divide (like cattle).
⚖️ 3. Metallic Money: Coins That Standardize Value
The next leap forward came with metal coins, often made from silver, gold, or copper. Civilizations such as the Lydians in modern-day Turkey were among the first to mint standardized coins.
🪙 Key Features
- Made from precious metals with inherent value
- Stamped with images and denominations
- Durable and easy to carry
🏛️ Real-World Use
- Ancient Greece and Rome used coins to build entire economies
- Trade flourished because value was now measurable and portable
💵 4. Paper Money: The Rise of Fiat Currency
As economies expanded, carrying heavy coins became impractical. The Chinese during the Tang Dynasty (7th century) were among the first to introduce paper money—a game-changing innovation.
💸 What Is Fiat Money?
Fiat money has no intrinsic value; it’s backed by trust in a government. A modern banknote doesn’t have gold behind it—but we believe in its value because the government guarantees it.
🌍 Global Use
By the 20th century, almost every country adopted paper currency.
- U.S. Dollar
- Euro
- Japanese Yen
These currencies became global trade standards.
💳 5. Plastic Money: Cards That Replace Cash
In the 1950s, the world saw another transformation—plastic money in the form of credit and debit cards.
💼 The Card Revolution
- First credit card: Diners Club (1950)
- Soon followed by Visa, Mastercard, and American Express
Plastic money offered:
- Convenience
- Security
- The ability to buy now, pay later (credit)
📲 6. Digital Money: The Cashless Economy
We now live in the era of digital money. Physical cash is still in use, but smartphones and internet banking have enabled seamless cashless transactions.
💡 Types of Digital Money
- Bank transfers
- Mobile wallets (PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay)
- QR code payments (widely used in China via Alipay & WeChat Pay)
Digital money offers:
- Instant payments
- Online shopping ease
- No need for physical wallets
🪙 7. Cryptocurrency: The Future of Decentralized Money
The newest stage in the development of money is cryptocurrency, introduced by Bitcoin in 2009. Unlike traditional money, it’s not controlled by any government or central bank.
🌐 Features of Cryptocurrency
- Decentralized (runs on blockchain)
- Limited supply (e.g., 21 million Bitcoins)
- Transparent and secure
🚀 Examples
- Bitcoin: The original and most well-known
- Ethereum: Offers programmable contracts
- Stablecoins: Pegged to fiat currencies like the U.S. Dollar
While it’s still evolving, crypto is already changing how people invest, trade, and even earn.
📊 Comparison Table: Stages of Money Development
| Stage | Key Feature | Medium Used | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barter | Direct exchange | Goods & Services | Wheat for Shoes |
| Commodity Money | Intrinsic value objects | Salt, Shells, Livestock | Cowry shells |
| Metallic Money | Standardized coins | Gold, Silver, Copper | Roman Denarius |
| Paper Money | Government-backed notes | Fiat Currency | Chinese Yuan, USD |
| Plastic Money | Card-based transactions | Credit & Debit Cards | Visa, Mastercard |
| Digital Money | Online payments | Mobile Wallets | PayPal, Alipay |
| Cryptocurrency | Decentralized digital | Blockchain Tokens | Bitcoin, Ethereum |
🧠 Why Understanding These Stages Matters Today
Money isn’t just currency—it reflects how we trust, trade, and communicate value in society. Each stage of its development was born from a need for efficiency, security, and convenience.
As we move forward, we’re likely to see even newer forms of money driven by artificial intelligence, biometrics, and decentralized finance (DeFi). Already, AI-based investment platforms and tokenized assets are blending financial tools with tech.
❓FAQ: Common Questions About Money Development
Q1. What is the oldest form of money?
Barter trade was the earliest, but the first official currency was metal coins by the Lydians in 600 BC.
Q2. Is cryptocurrency real money?
Yes, though not universally accepted, it functions as digital money and is used in transactions and investments.
Q3. Why was paper money invented?
To replace heavy coins and offer a lighter, more efficient method for trade and commerce.
Q4. Will we become a completely cashless society?
In many parts of the world, we’re nearly there. Mobile payments and digital banking have already minimized the need for physical cash.
Q5. What’s the difference between fiat money and cryptocurrency?
Fiat is government-backed and controlled by central banks; crypto is decentralized and based on blockchain technology.
🔚 Final Thoughts: From Cows to Crypto
The story of money is one of human innovation. It shows how far we’ve come in building systems of trust, value, and convenience. Understanding its evolution helps us prepare for what’s next—whether it’s digital yuan, Bitcoin, or AI-generated currencies.
Money will keep evolving. The question is—how ready are we for the next change?